October is breast cancer awareness month. As a Certified Lymphedema Therapist, I have decided to blog about lymphedema, a potential complication of certain breast cancer treatments.
By way of introduction, allow me to share some background information. In western societies, breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed tumor among women. In fact, 27% of tumors diagnosed among women are breast tumors. Fortunately, minimally invasive surgeries (including sentinel or axillary lymph node dissection) have become extremely popular. However, as with any surgical procedure, internal scarring and adhesions may develop which may affect upper extremity joint and muscle function. Furthermore, removal of lymph nodes may result in dysfunction of the lymphatic system, as will be discussed below.
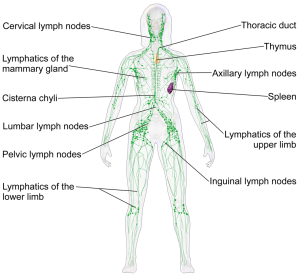
Approximately 10% of water that exits the circulatory system at the cellular level does not return at the venous end of capillaries due to pressure related factors. This excess water is called the lymphatic load. It enters the lymphatic system at lymphatic capillaries, and it is returned to the circulatory system at the venous angle (the junction of the left subclavian vein and the internal jugular vein). The lymphatic system also allows for transport of certain particles (including fats from the digestive system and certain large proteins) that are too large to travel through the circulatory system.
Lymph nodes are small oval shaped organs that contain white blood cells, T cells, and B cells (which are responsible for fighting infection and are a component of the immune system). Lymph fluid travels through a series of lymph nodes, where filtration of the load occurs. There are approximately 600 lymph nodes in the average adult human body.
Dysfunction of the lymphatic system can result in lymphedema, swelling of the upper or lower extremities due to an impaired lymphatic system. Lymphedema can also develop in the trunk, head, neck, or genitals. It is a chronic disease and treatment involves lifetime management of the condition.
Primary lymphedema involves a congenital malformation of the lymphatic system (ex. the vessels are too large or small) resulting in lymphedema. Secondary lymphedema is when an initially healthy lymphatic system can develop problems through infection, obstruction, or damage. Globally, the most common cause of lymphedema is filariasis, a parasitic disease that is caused by thread-like roundworms which occupy the lymphatic system. The worms enter the lymphatic system through blood feeding mosquitoes and black flies in certain tropical countries.
In the United States, the most common cause of lymphedema is breast cancer-related surgeries that involve removal of affected axillary lymph nodes. Removal of lymph nodes disrupts the normal return of fluid to the venous angles. This can result in swelling of the involved upper extremity. Similarly, lower extremity lymphedema can develop after removal of pelvic and or inguinal lymph nodes (ex. due to prostate or gynecological cancer surgeries).
Lymphedema can develop days, weeks, months, or even years after surgical node removal. Therefore, individuals who have undergone these types of surgeries should be aware of their predisposition towards developing the disease. Any abnormal swelling or changes should be reported to one’s physician immediately, because the prognosis is better if the disease is detected and treated as soon as possible. The gold standard of care to treat lymphedema is complete decongestive therapy (CDT). CDT consists of four components:
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
- Compression
- Exercises
- Skin Care
MLD was pioneered by Dr. Emil Vodder in the early 1900s, and it is series of manual techniques (including “pump,” “rotaries,” “scoop,” “and pump-push”) which promote mobilization of excess lymph fluid from the distal extremities towards proximal, healthy open lymph channels. Another way to think about lymphedema due to lymph node removal is that there is congestion on one “road”. Therefore, the certified lymphedema therapist (CLT) seeks to create new channels on uncongested “roads,” thereby creating detours for the lymph to return to the venous system through alternate routes. MLD allows the CLT to direct the lymph along healthy, open lymphatic pathways.
Revitalize Physical Therapy recognizes that the breast cancer fight might not fully end after surgery. As a therapist trained in CDT and MLD, it would be an honor and privilege to help address lymphedema experienced by you or a loved one. Please contact us if there is anything we can do to help.


