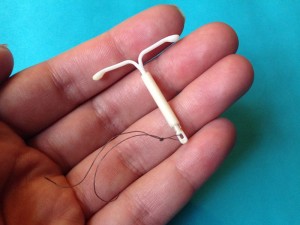
Isn’t it wonderful when you can kill two birds with one stone? A recent study in the medical journal Obstetrics & Gynecology (November 7, 2017) posits that intrauterine devices (IUDs), a popular form of contraception, may in fact do just that. Not only do they prevent unwanted pregnancy, but they may decrease a woman’s risk of developing cervical cancer by approximately thirty percent.
IUDs trigger an immune response which destroy sperm, thereby preventing them from fertilizing female eggs. (For more information on IUDs and how they operate, please refer to my previous blog, IUD-etails, December 2015.) This recent study proposes that not only does this immune response kill sperm, but it also kills human papillomavirus (HPV), the virus which is strongly correlated with development of cervical cancer.
These findings are particularly promising for women who have not received the HPV vaccine. The HPV vaccine is limited in the sense that it can only protect a woman who has never been exposed to the virus. Vaccination at a young age allows females to develop a strong immune response to combat the virus upon first exposure. Due to the high prevalence of HPV (which is often asymptomatic in males who may then transmit the virus to females), the vaccine is presently being routinely administered to females as young as 11 years old. Unfortunately, this trend is relatively new, and many women in their 30s, 40s, and beyond have already been exposed to HPV. The presence of HPV increases one’s risk of cervical cancer.
Up until last week, there wasn’t much to offer or recommend to women previously exposed to the virus. However, this promising research may suggest that IUD implantation may significantly decrease the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Will IUD usage become the new prophylactic trend for women with HPV to prevent cancer? Only time and additional research will tell. Even if this will be the case, IUDs should not replace routine Pap testing nor HPV vaccination. However, these exciting findings may shape and improve the future of women’s health and disease prevention.